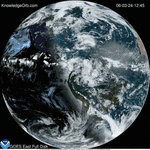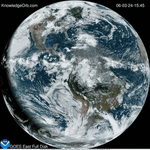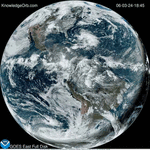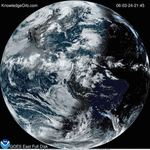
(NASA) Early Wednesday morning, at 3:27:20 AM Eastern Time, a piece of an asteroid, about 2 feet in diameter and…
Category: Space
Comet PANSTARRS Video as it passes Earth…Amazing.
Comet PANSTARRS, with Earth flying through space (stationary dot center+right), deep space stars background, and solar particles emanating from the…
Cool LOW Flyby Video of Saturn Moon Lapetus
Flying Down Lapetus Spine Animated GIF made from 14 frames shot by the Cassini spacecraft as it passed over Saturn’s…
Chandra sees giant black hole ejecting material.
(NASA) – Astronomers using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory have taken a major step in explaining why material around the giant…
Awesome image of light year long vapor trail
(NASA) – Harsh winds from extremely bright stars are blasting ultraviolet radiation at this “wanna-be” star and sculpting the gas…
New Nova Delphini 2013 Naked Eye Visible!
UPDATE 8/19/13 The NOVA appears to have peaked at about magnitude 4.2 and has decreased but seems stable. This plot…
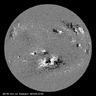
Magnetic Poles of Sun about to flip, Solar Max Near
(NASA) According to recent measurements the magnetic field of the Sun is about to change indicating were very near the…
NASA Voyager Spacecraft Close to Touching Face of God?
In 1977 NASA and mankind sent two emissaries into the great expanse of the universe. As they travel do they…